Let's Design your Custom Ring. Call us at (212) 522 9918
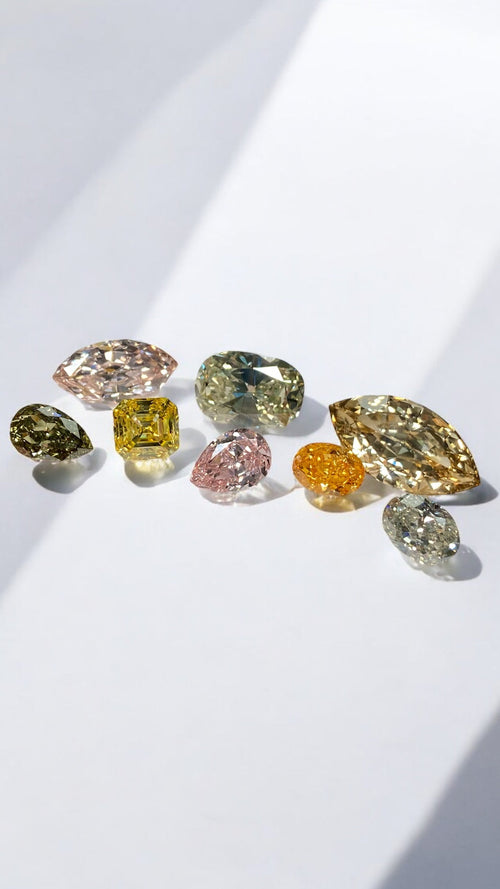
What are champagne diamonds?
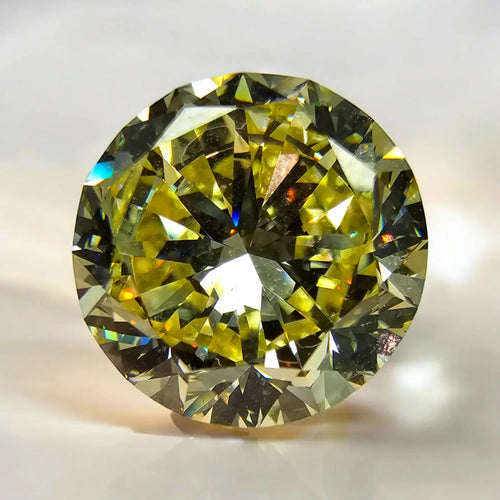
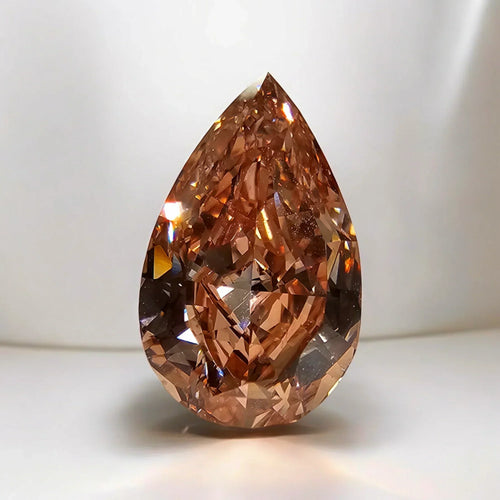
Champagne diamonds, also known as "cognac" or "brown" diamonds, are a fascinating category of diamonds characterized by their warm, earthy hues ranging from light beige to deep brown. These diamonds get their name from the resemblance of their color to the golden tones of champagne, evoking images of luxury and sophistication.
However, beyond their aesthetic appeal, champagne diamonds have unique geological and chemical properties that distinguish them within the spectrum of natural diamonds. Let's explore in high detail what champagne diamonds are, delving into their formation, characteristics, and significance within the gemstone industry.

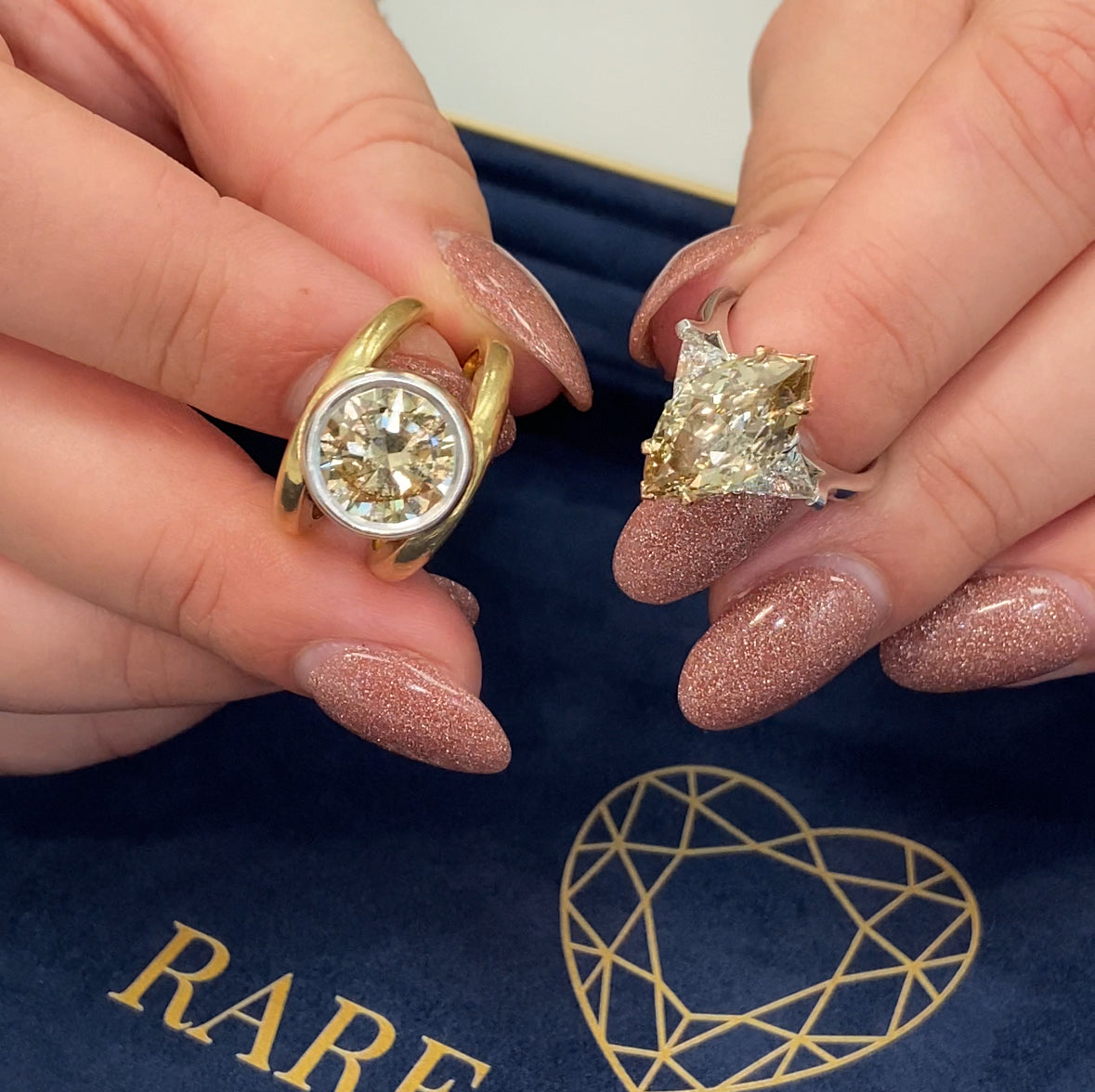
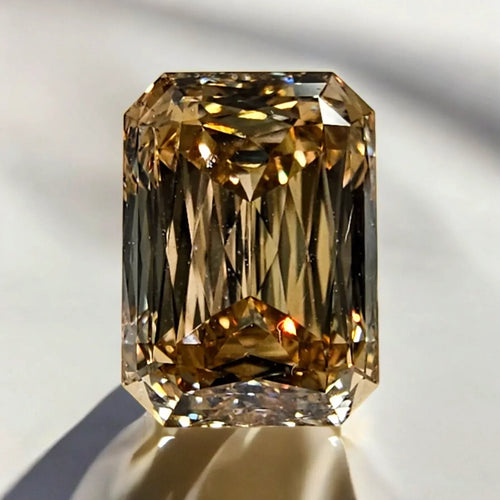
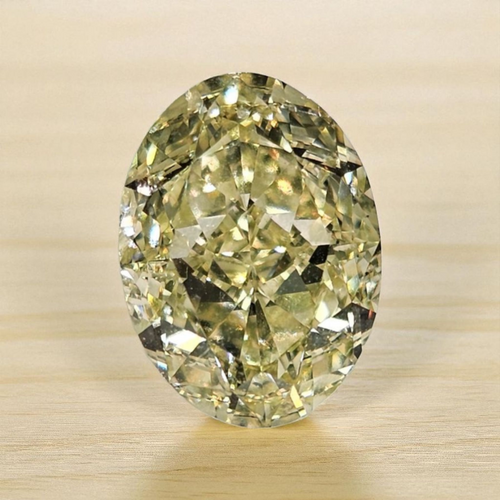
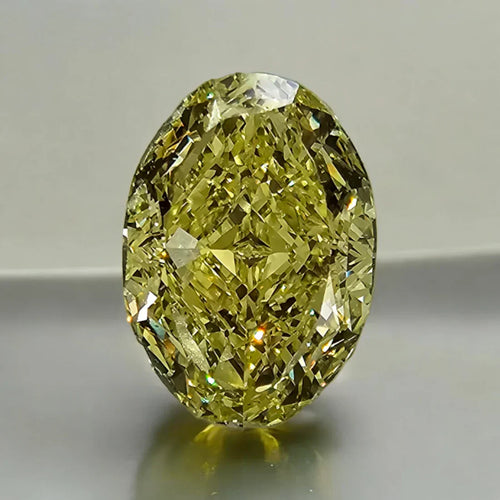
This is one of our most impressive, and lively, natural champagne diamonds, a 4 Carat GIA Certified 'Fancy Brown-Yellow' with VS1 Clarity.
What makes a champagne diamond?
How are natural champagne diamonds formed?
Geologically, champagne diamonds are often associated with specific diamond deposits, such as those found in the Argyle mine in Western Australia, which has been a significant source of these diamonds. The geological conditions and the presence of certain minerals during diamond formation contribute to the unique coloration observed in champagne diamonds.
The color of champagne diamonds results from the presence of nitrogen impurities and structural anomalies within the diamond lattice. These imperfections absorb light in the blue spectrum, imparting the distinctive brownish hues observed in champagne diamonds. The intensity and distribution of these color-causing elements determine the overall color appearance and value of the diamond.
Color and Grading of Natural Champagne Diamond
In the Gemological Institute of America (GIA) color grading system, champagne diamonds are typically classified within the brown color range. The color grade assigned to champagne diamonds by the GIA is represented by letters, with variations depending on the intensity and tone of the brown hue. The color scale for brown diamonds typically ranges from light to dark, with the following letter grades commonly used:
-
Light Champagne: These diamonds may have a faint to light brown hue. In the GIA color grading system, they may be classified as "K" or "L" color grades.
-
Fancy Champagne: Diamonds with a more pronounced brown hue fall within the "fancy" category. Fancy champagne diamonds may receive color grades ranging from "M" to "Z" on the GIA scale, depending on the depth and saturation of the brown coloration.
-
Cognac and Chocolate: As the brown color intensifies, champagne diamonds may be described as "cognac" or "chocolate." These diamonds may receive color grades from "N" to "Z," with deeper tones falling toward the latter end of the alphabet.
It's important to note that the color grading of diamonds is based on their body color, which refers to the dominant hue observed in the stone. Champagne diamonds may also exhibit secondary hues, such as pinkish or yellowish undertones, which can influence their overall appearance and value. However, the primary color letter assigned to champagne diamonds reflects their brown coloration within the GIA color grading system.

Where are natural champagne diamonds found?
Natural champagne diamonds are mainly found in the Argyle Diamond Mine in Western Australia. This mine, located in the East Kimberley region of Western Australia, has been renowned for producing a significant portion of the world's champagne diamonds. The Argyle mine has been operational since 1983 and has been particularly known for its production of colored diamonds, including pink, red, and brown hues.
However, it's important to note that the Argyle mine ceased its operations in November 2020, marking the end of an era for champagne diamond production. As a result, champagne diamonds from the Argyle mine have become increasingly rare and sought after in the gemstone market.
While champagne diamonds can be found in other regions around the world in smaller quantities, the Argyle mine has historically been the primary source of these unique gemstones. As a result, Argyle champagne diamonds hold a special significance within the diamond industry, symbolizing rarity, quality, and the legacy of one of the most iconic diamond mines in the world.
Are champagne diamonds more valuable than white diamonds?
The value of champagne diamonds, like all colored diamonds, is influenced by the intensity and quality of their color. Champagne diamonds range from light straw to deep cognac hues, with variations in saturation and tone. Intense and vivid champagne diamonds with rich, uniform coloration are generally more valuable than lighter or less saturated stones. Factors such as color consistency, absence of undertones, and overall appearance play a significant role in determining the value of champagne diamonds.
While white diamonds remain a timeless classic and are often favored for engagement rings and formal jewelry, colored diamonds, including champagne diamonds, have gained a lot of popularity among those looking for unique jewelry options.
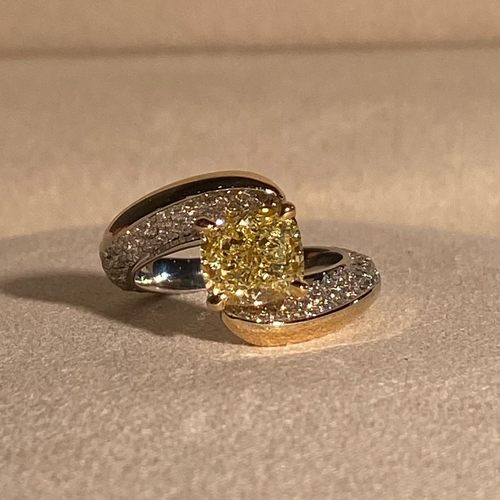
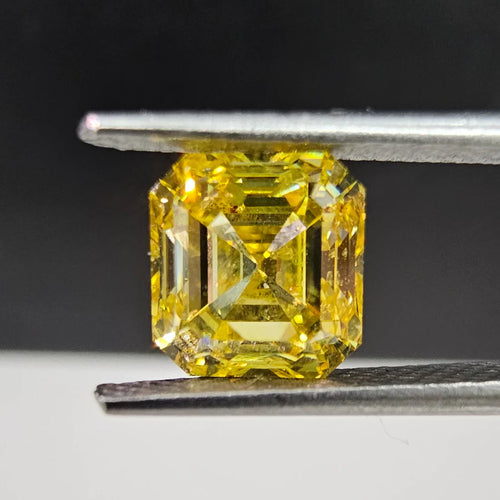
What diamond cuts do natural champagne diamonds come in?
Champagne diamonds can come in almost any shape or size! Some of the most common shapes in which champagne diamonds are available include:
Round Brilliant Natural Champagne Diamond

Oval Cut Natural Champagne Diamond

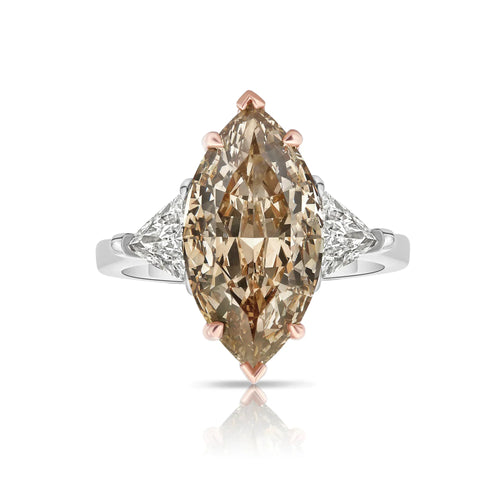
Marquise Cut Natural Champagne Diamond

Take a look here at the champagne diamonds we have at Rare Colors!